New respiratory virus vaccines [Scripps]
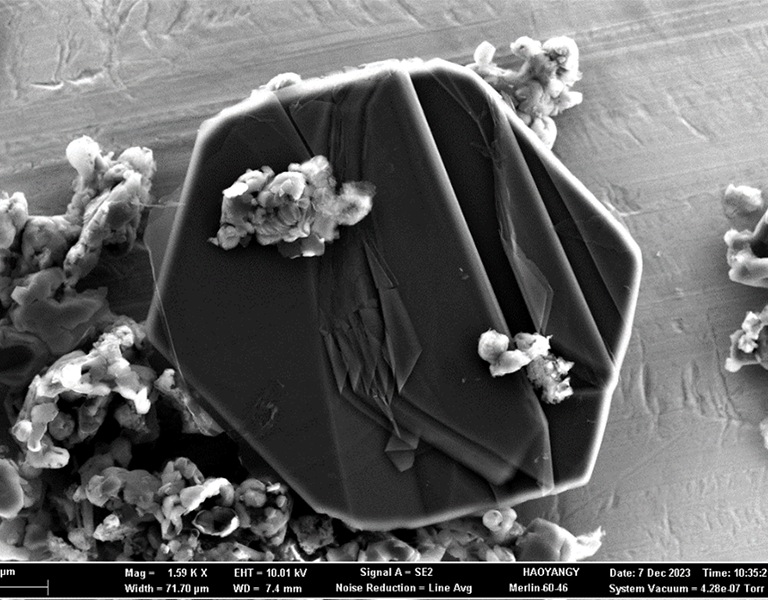
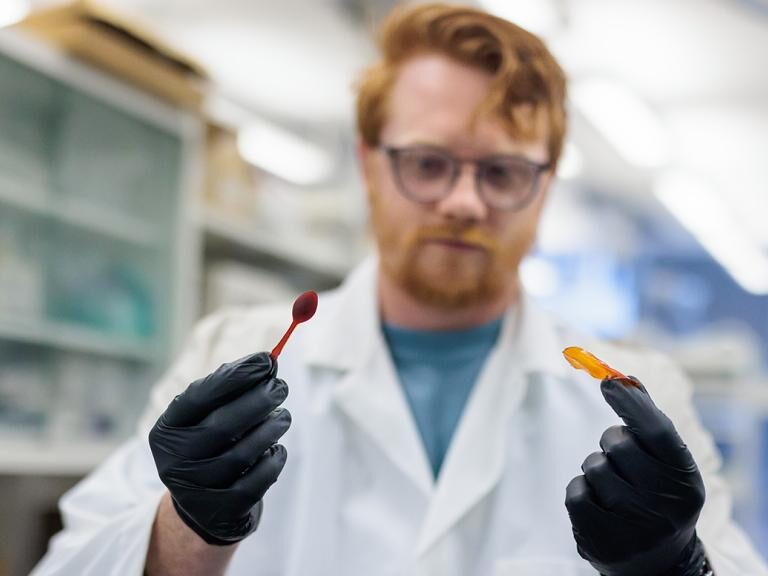
In most people, the lung-infecting pathogens known as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human metapneumovirus (hMPV) trigger mild cold-like symptoms. But in infants and seniors, these viruses can cause severe pneumonia and even death. Vaccines against both viruses, however, have been difficult to design. Now, Scripps Research scientists have analyzed the structure and stability of …